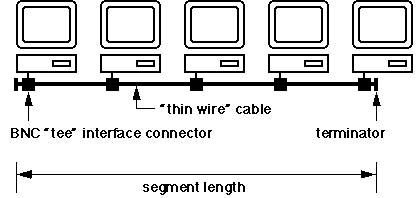
A thin wire (coaxial cable) segment had a maximum length of 185 metres, plus a few other rules as to numbers of machines, and the distance between them. The 185m segment length can be extended using a repeater[3], which behaves somewhat like a bi-directional amplifier. The resulting extended LAN acts like a single larger segment, and is referred to as a "collision domain", because every computer in each of the component segments still "sees" everyone else's tranmissions.
| Lecture 14: Multiaccess Networks | Copyright © 2005 P.Scott, La Trobe University Bendigo. |