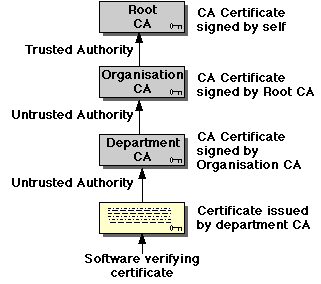
More complex applications will involve certificates issued (for example) for use within an organisation, or department. In this case, a certificate is signed by its issuer. In order to establish the validity of the issuer's signature, the application may need to obtain the issuer's CA certificate as well, which is, in turn, signed by the next higher authority -- verifying a certificate chain. Note that the root CA is implicitly trusted -- as soon as the client software encounters a certificate signed by this CA, authentication is complete.
| Lecture 18: Encryption #3 -- Practical Encryption | Copyright © 2003 P.Scott, La Trobe University Bendigo. |