previous |
start |
next
Public Key Authentication
This is the technique by which an entity verifies that her
communication partner is who he purports to be and not an imposter.
Authentication can be easily achieved if both parties share a
common secret key or keys, (eg, typical password authentication)
however it's much more nicely done using Public Key
cryptography:
Public key cryptosystems can provide authentication if, in
addition to:
P = D ( E ( P ) )
we also have:
P = E ( D ( P ) )
This is true for RSA. Now consider Alice, who wishes to
authenticate herself to a communications partner Bob. Bob already
knows Alice's public key.
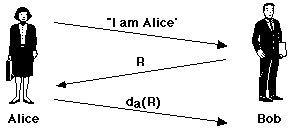
Alice announces to Bob that she wishes to communicate. Bob responds
by choosing a large, single-use random number R
(sometimes called a nonce) which he sends to
Alice. Alice encrypts the random number using her private
key, da and returns the
encrypted value to Bob. Bob applies Alice's public
key to the returned value, and if it decrypts to
R then he can be certain of the identity of his
communication partner. It's obvious that this protocol could be
extended to verify the identity of Bob as well.
previous |
start |
next
